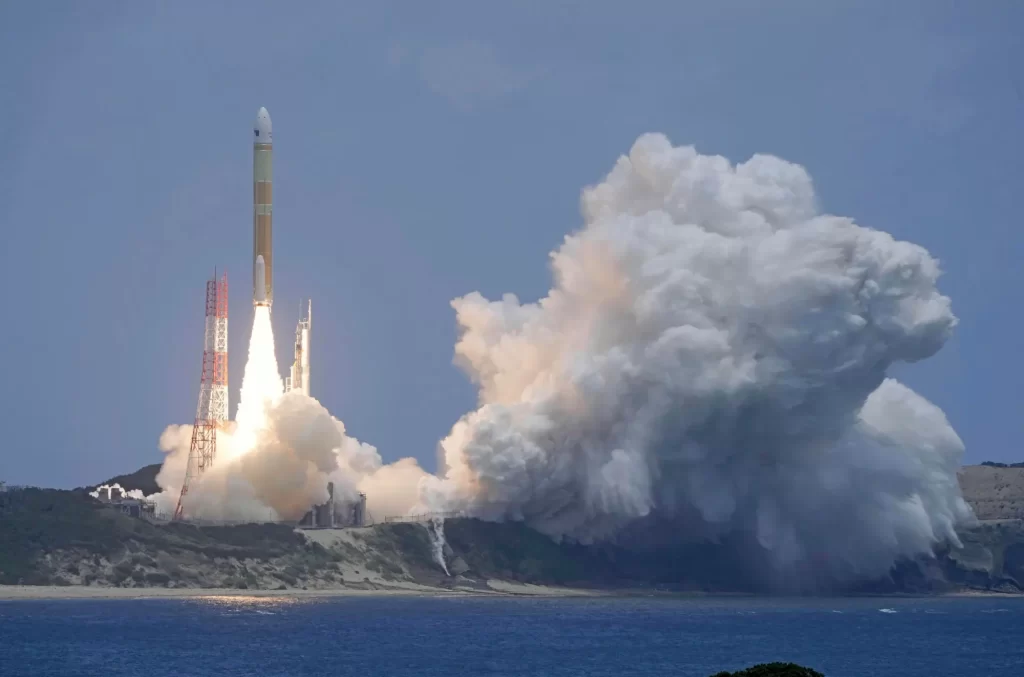
Japan deployed an upgraded Earth observation satellite for disaster response and security after it was launched on a new flagship H3 rocket Monday.
The H3 No. 3 rocket lifted off from the Tanegashima Space Center on a southwestern Japanese island and released its payload about 16 minutes later as planned, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA, said during a livestream.
The Advanced Land Observation Satellite, or ALOS-4, is tasked primarily with Earth observation and data collection for disaster response and mapmaking. It’s also capable of monitoring military activity, such as missile launches, with an infrared sensor developed by the Defense Ministry.
The rocket appeared to fly as planned, and JAXA is expected to give further details at a news conference later Monday. The launch was initially planned for Sunday but was delayed due to bad weather at the launch site.
The ALOS-4 is a successor to the current ALOS-2 and can observe a much wider area. Japan will operate both for the time being.
The launch was the third of the H3 system, after the successful one on Feb 17. and the shocking failed debut flight a year earlier when the rocket had to be destroyed with its payload — a satellite that was supposed to be the ALOS-3.
Japan sees a stable, commercially competitive space transport capability as key to its space program and national security.
JAXA and its main contractor Mitsubishi Heavy Industries have been developing the H3 launch system as a successor to its current mainstay, H-2A, which is set to retire after two more flights. MHI will eventually take over H3 production and launches from JAXA and hopes to make it commercially viable by cutting the launch cost to about half of the H-2A.